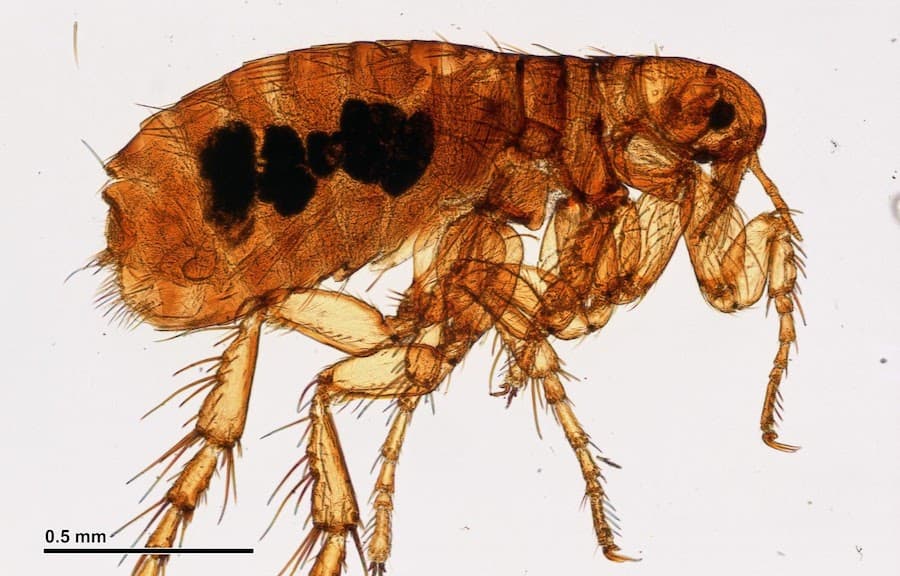
How to Treat and Get Rid of Flea Bites on Humans
Despite their minuscule size, fleas are capable of causing extreme irritation and can even transmit diseases to people. Therefore, it’s important that you know how to identify and treat flea bites to soothe itching and prevent further complications.
This article will examine how to distinguish flea bites from other insect bites, how long they last, how best to treat them and the potential risks you should be aware of.
How to Treat Flea Bites: The Best Methods
As we’ve seen, flea bites eventually go away on their own without any treatment. Still, that doesn’t help much when you’re struggling not to scratch until you bleed! Luckily, there are some effective home and over-the-counter treatments which calm the itch and soothe the skin, helping you to avoid an infection caused by scratching.
Before you use any of the following treatments, be sure to clean the bitten area thoroughly with soap and water.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is a popular remedy against fleas in the home, but can also be effectively used to soothe their bites. The application of apple cider vinegar can reduce swelling, inflammation, and itching. It also helps prevent infections, due to its antiseptic properties. Raw, unfiltered apple cider vinegar is the best choice for this treatment. If you experience irritation, diluting the vinegar should resolve this.
Method:
- Take a cotton ball and soak it in raw apple cider vinegar
- Place firmly upon the area of the flea bite but do not press too hard
- Hold in place for around five minutes before removing
- Repeat throughout the day as needed
Cold Compresses
Cold compresses are well known for their ability to lessen pain and swelling, especially when caused by sports injuries. Cold treatments are effective because they work to numb the skin, preventing the nerve endings from transmitting pain signals. Cold temperatures also constrict blood vessels which reduces inflammation.
Method:
- Take some ice cubes or an ice pack, and wrap them in a thin cloth or paper towel
- Apply firmly, but gently, to the affected area for a maximum of three minutes
- Remove and give the skin a rest for a few minutes
- Re-apply the compress for a further three minutes
- Continue in this way for 10-15 minutes
- You can use this method multiple times a day
Important: Do not apply ice directly to the skin, as this can cause ice burns
Witch Hazel Oil
Witch hazel is another fantastic home remedy for flea bites. This healing oil has astringent properties, which help to reduce irritation and inflammation by encouraging the pores to shrink. Furthermore, witch hazel can combat against infection, helping you to heal faster without scarring.
Method:
- Place a few drops of witch hazel into a dish
- Take a cotton ball and soak it in the witch hazel
- Dab the cotton ball onto any areas where you have been bitten
- Repeat several times a day as needed. If irritation occurs, dilute the oil
Neem
Neem is also known as Indian lilac. It’s extremely popular in traditional Indian medicine and many home remedies. The leaves of this plant contain effective antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties, which are great for calming flea bites. This plant is toxic to cats, so please keep this away from any kitties in your home.
Method:
- Take a handful of neem leaves and simmer them in a pan of water for 20 minutes
- Strain out the leaves and allow the mixture to cool
- Soak a cotton ball in the solution and place on the flea bite
- Hold in place for around 15 minutes
- Repeat every few hours for a couple of days or until the bite stops itching
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is a well-known home remedy and popular treatment for many ailments. The use of pure, fresh aloe vera gel can accelerate the healing of flea bites. It has moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties which work quickly to calm the skin and reduce swelling. It is so effective for treating skin problems, that it’s often used as a natural alternative to some pharmaceutical creams.
Method:
- Cut a small piece of leaf from an aloe vera plant
- Gently squeeze the leaf to extract the gel
- Gently rub this onto any flea bites
- Leave on the skin for 15 minutes
- Rinse well with warm water
- Repeat this method up to three times a day
- Keep the remaining leaf in the fridge until the gel is exhausted
Note: You can also use pre-packaged aloe vera gel if you cannot access a plant.
Baking Soda
Baking soda is a convenient and cheap home remedy for flea bites. Almost every home will have some baking soda in the pantry, so it makes for a quick and easy solution for itchy and sore skin. Baking soda has anti-inflammatory properties, as well as antimicrobial benefits, which can help protect against infection.
Method:
- Add a teaspoon of baking soda to a bowl, containing a few drops of water
- Mix with a fork to make a thick paste
- Add more water as you need
- Smooth the paste onto the flea bites and any reddened skin around them.
- Leave the mixture on the bites for around 15 minutes.
- Rinse off with warm water.
- Repeat up to four times a day as needed.
Oatmeal
Oatmeal is another useful remedy for skin issues and is found in most household cupboards. Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory and moisturizing benefits that soothe and calm itching and swelling skin. It has this effect due to the way it balances skin pH levels. This locks in moisture and calms irritation.
Method:
- Grind one cup of oatmeal into a fine powder. You can use a food processor or a pestle and mortar for this
- Add an equal amount of yogurt to the ground oatmeal and mix well to make a paste
- Smear a thick layer of the paste over the irritated areas of skin
- Leave in place for as long as 30 minutes
- Rinse away with lukewarm water
- Repeat three times a day until itching has ceased
If you have many bites which are driving you crazy, you can take an oatmeal bath to soothe the itching. Prepare a warm bath and add one cup of ground oatmeal into the bathwater. Soak in the bath for as long as you wish. Do not add any bubble bath or soap when using this method, as it can interfere with the effectiveness of the oatmeal.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines help to stop allergic reactions and extreme irritation by blocking a substance called “histamine” from affecting your body. Histamine is a defensive chemical which is released when the body detects a threat, such as a potential infection. It makes the blood vessels in the area expand, causing swelling, which is designed to defend the body from further harm.
However, for people who have allergies, their body often overreacts to what it perceives as an external threat. This results in an extreme reaction to minor irritants. Using antihistamines can reduce the reaction to insect bites, calming the swelling and itching quickly and effectively.
There are two kinds of antihistamine tablets: drowsy and non-drowsy. The older forms of antihistamines tend to make people feel a bit sleepy. These are hydroxyzine, chlorpheniramine, and promethazine. Newer formulations are much less likely to induce drowsiness. These are fexofenadine, cetirizine, and loratadine.
Antihistamines are available in a variety of different forms; capsules, tablets, creams, gels, lotions, syrups, and even nasal sprays. For flea bites, it is best to select a topical formula that can be applied directly to the skin.
You can purchase many antihistamine products over the counter at your local pharmacy.
What Do Flea Bites Look Like?
There are a wealth of bugs out there that like to bite, sting, and feed on humans. As a result, it can end up being a little difficult to determine which creature is the culprit when you start to itch.
The first thing to consider is the possibility that you’ve been subjected to the presence of a pesky flea or two. If you have pets in the home, or have been recently visited by someone who has a pet, the chances are high that you’ve been exposed to one of these bloodsuckers.
Fleas do not like to live on humans. We are simply not hairy enough, which makes it difficult for fleas to ‘cling on’ to us. They also much prefer cat and dog blood to ours. Therefore, flea bites on humans occur when the hitchhikers on your furry friend get dislodged and become desperate for a meal. If fleas are brought into the home by a friend’s dog and left behind, they will simply have no choice but to bite you.
Fleas will take the opportunity to feed upon you wherever they can reach the skin. The most frequently bitten areas are often the feet and ankles, simply because these are the parts of the body closest to the ground. If you have itchy bites in these areas when you have been indoors, fleas are a top suspect.
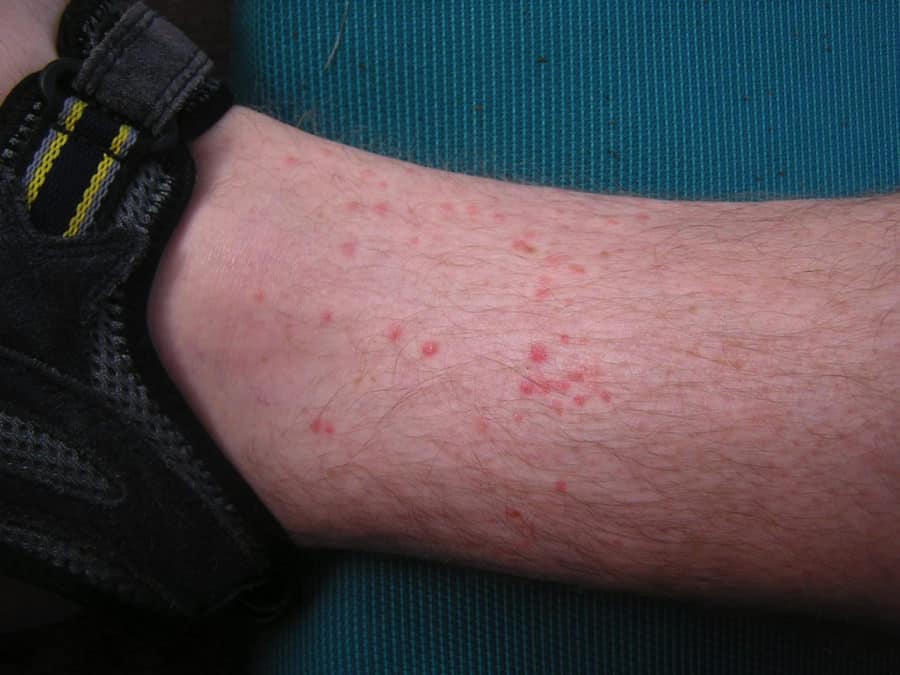
A flea bite will initially look like a small area of raised skin, almost like a pimple beneath the surface. After 24 hours, these patches of skin begin to look like little welts. Often, there is a halo of redness around the center of the bite. It’s common to have groups of several bites in one area.
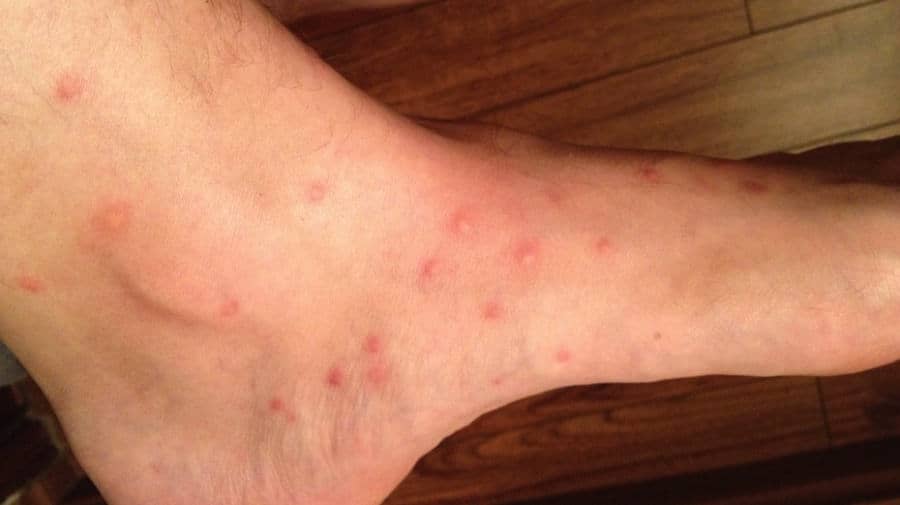
The intensity of the irritation and pain caused by a flea bite depends heavily upon the person and their individual sensitivity. What causes one person extreme itchiness may not be noticed by another. In most cases, flea bites and the body’s reaction to them corresponds to an individual’s previous contact with fleas. Over time, your immune system can build up a defense against flea bites.
In most people, a flea bite will not elicit an immediate reaction like a wasp or bee sting. There is almost always a delayed reaction by the body. Children may have very delayed reactions to flea bites, so if you spot flea bites on your child, they may not have occurred within the last few hours.
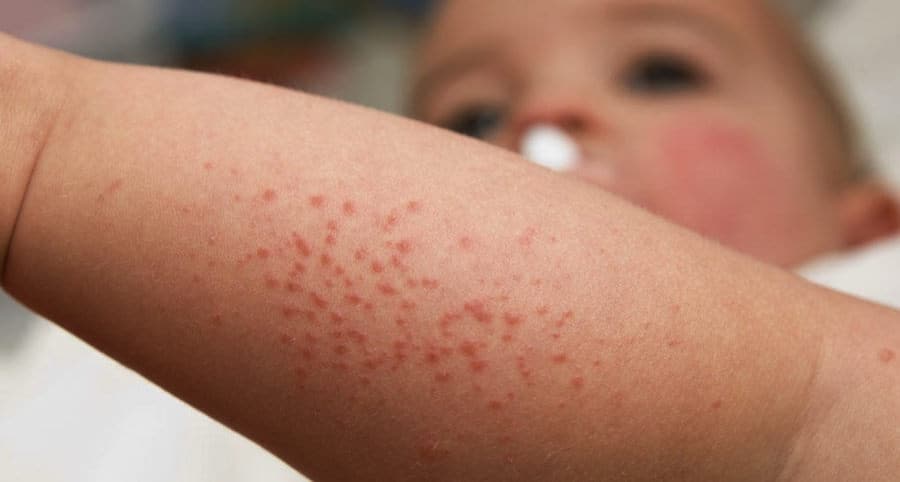
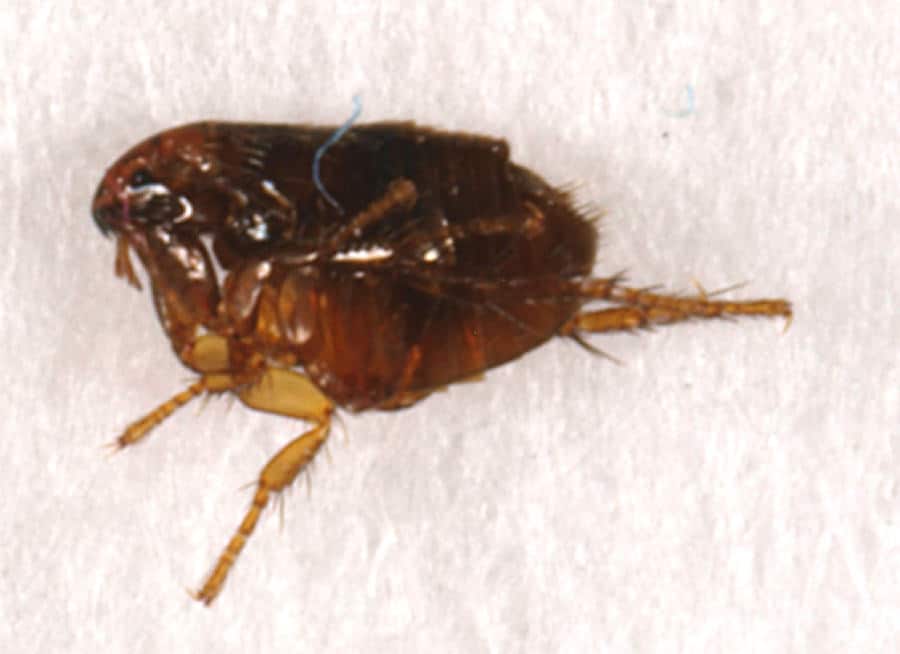
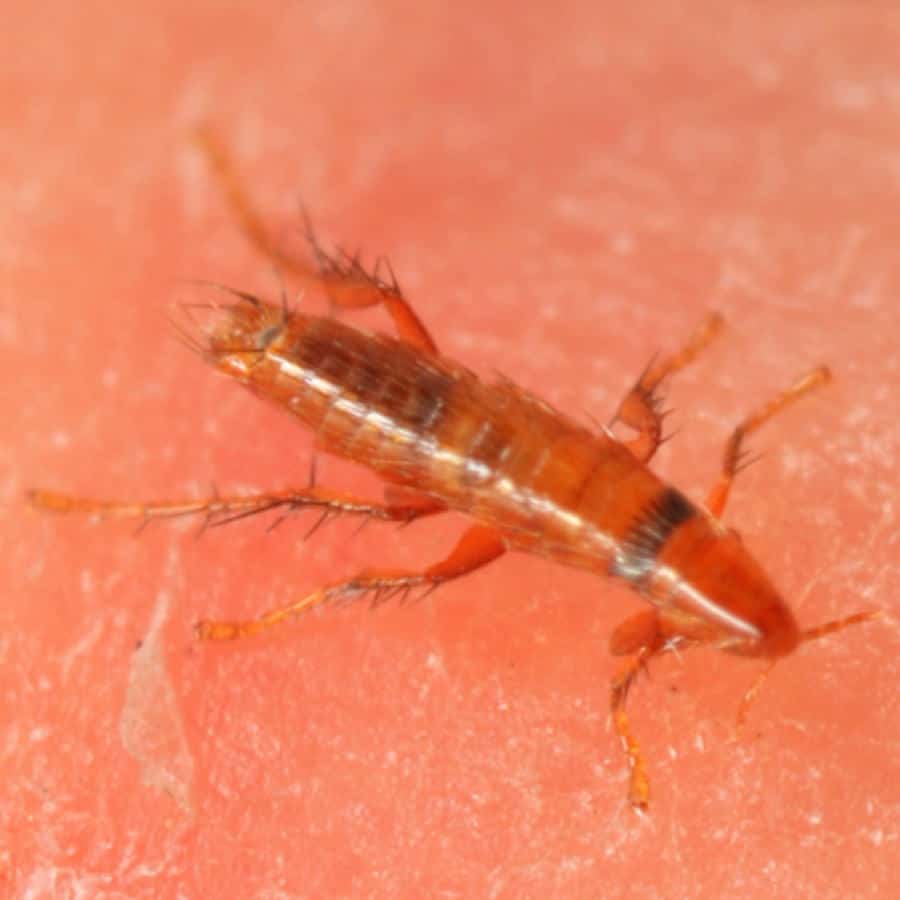
Once a flea has landed upon bare skin, it will start to undertake “exploratory probing” by piercing the skin in multiple locations, seeking a suitable blood vessel. Once a vessel is located, they secrete saliva which has anticoagulant properties to keep blood flowing.

It is the exploratory probing which results in the appearance of multiple bites in one place. Flea saliva is the main cause of irritation and allergic reactions from flea bites.
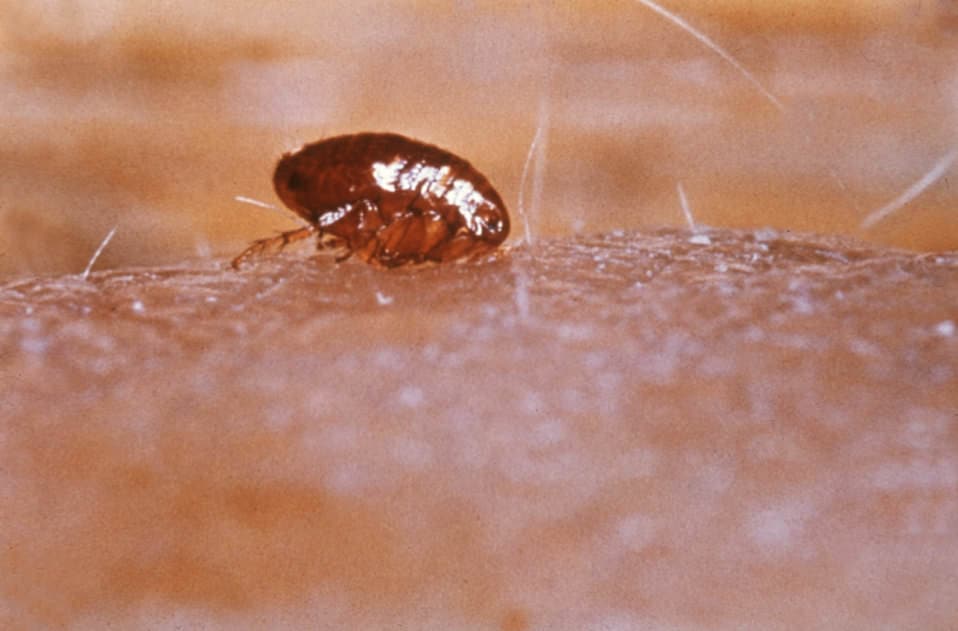

If they are not disturbed, female fleas will feed for as long as 25 minutes, while males feed for about half this time. When they have finished feeding, the site of the bite will begin to become raised within 30 minutes. The skin around this raised area will often turn red as a result of capillaries dilating in response.
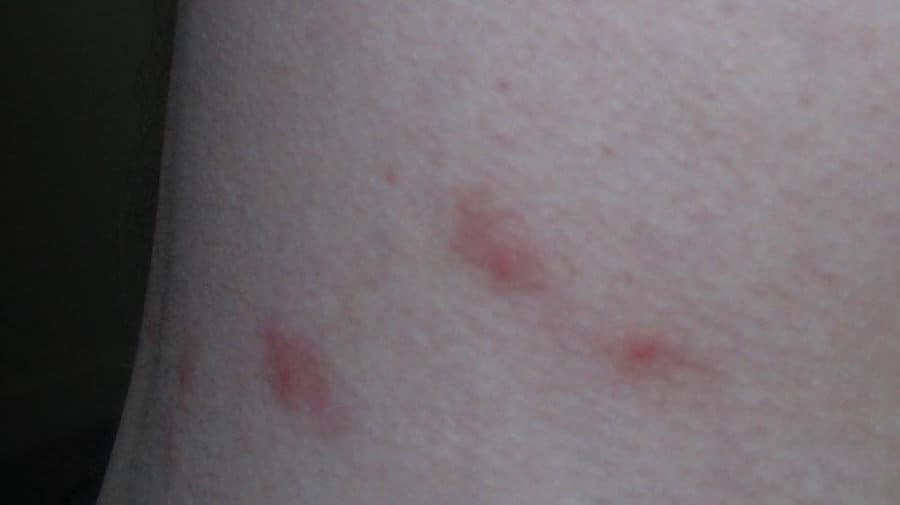
Swelling caused by flea bites can have an irregular shape, so it can be hard to locate the exact spot where the bite occurred. Sometimes, there will be a “halo” of darker redness around the perimeter of the bite.
The initial swelling from a flea bite is usually between 0.07 inches and 0.3 inches across at the widest area. Occasionally, the redness can spread as far as 0.7 inches from the bite location. The inflammation reaches its peak a couple hours after a bite, but normally fades away to nothing within 12 hours.
At this stage, flea bites appear as little red dots on the skin; they are generally not noticed by the victim until they start to itch. Sometimes intensive scratching will open a hole in the skin which can lead some to believe the open area has been caused by the flea. This is not the case.
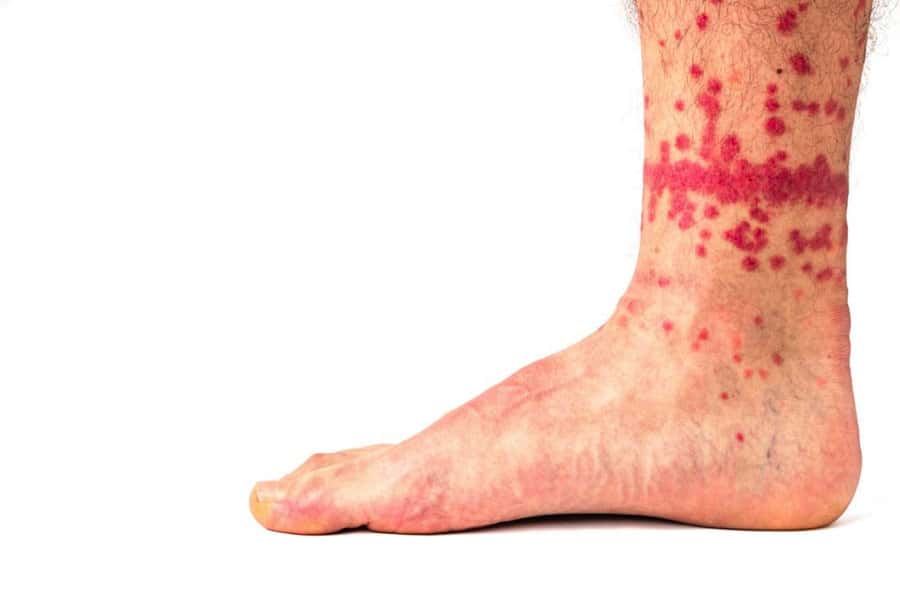
Many people get confused when trying to identify flea bites from those of other insects, such as mosquitoes. Mosquito bites are often much more “puffy” and fluid-filled than flea bites, but this also depends on the skin of an individual and the species of mosquito which has bitten.
If you have recently been spending time outdoors during the morning or evening around sunset, or have been near wetlands or streams, there is the potential you are suffering from mosquito bites. These bites tend to be bigger and more widely spread than flea bites, which are clustered in a small area.
With regard to the difference between bed bug bites and flea bites; bed bug bites are surrounded by a rash and present in straight lines of multiple bites, not clusters like flea bites.
How Long Do Flea Bites Usually Last?
Immediately after you receive a flea bite, the first thing that occurs is a rising of the skin in the affected area. This is known as “whealing.” Wheals tend to settle completely within a few hours and do not cause any irritation.
Within 12 hours of being bitten, the wheal will have been replaced by a “papule.” These are firm, swollen bumps, which are red and inflamed. These papules are incredibly itchy. The sensation will continue to increase in intensity until peak irritation occurs about 24 hours after the bite took place.
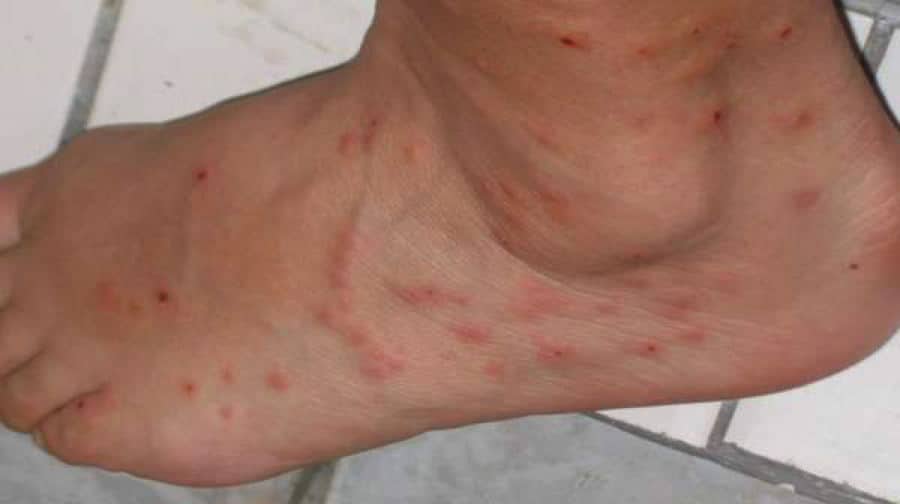
Itchy papules start to diminish 48 hours after being bitten and are usually completely gone after 72 hours. However, in some cases, these papules can remain for as long as 14 days. Once the papule has gone, it will leave a faint red mark which stays visible for around a week.
Individuals who have a tendency to allergic reactions usually suffer a more intense skin response to flea bites. These people experience a delayed reaction before blisters form in the area where the bite took place. This skin response is painful and irritating, but usually reaches its peak about 3 days after the individual suffered the bite.
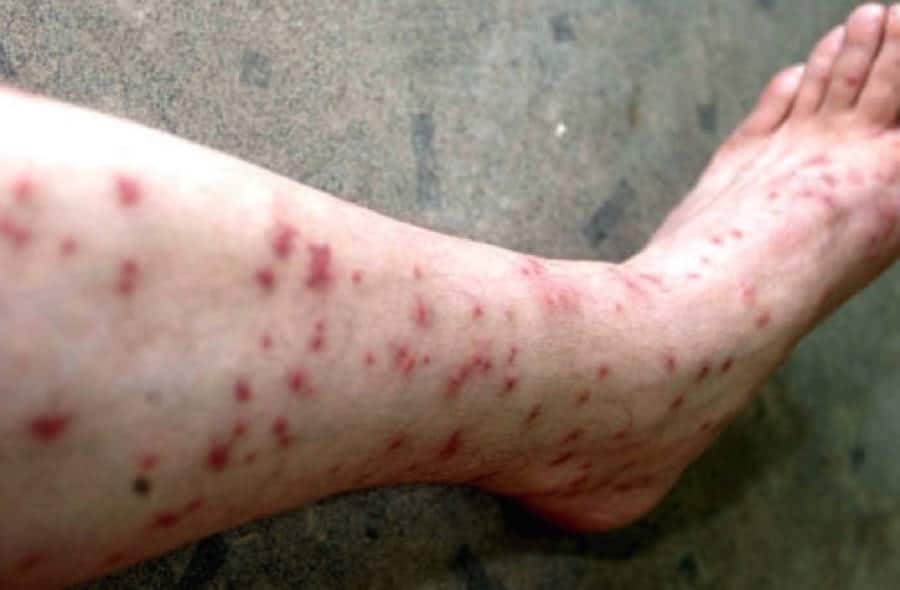
It’s important to keep bites clean, and try to avoid scratching or rubbing them. Intensive scratching can break open the skin, releasing the protective healing fluid within the wound and increasing the risk of infection and scarring.
Infected flea bites become filled with pus and take on the appearance of a large pimple or boil. If infection occurs, the wound will take much longer to heal, sometimes as long as 6 weeks. Even after healing, uneven pigmentation of the skin can persist for months afterwards.
The majority of people will only suffer the effects of a flea bite for a couple of days. However, there are rare occasions when certain individuals will experience extreme reactions that can last for many weeks. There are reports of cases where exceptionally sensitive people still have evidence of previous bites after 12 months have passed.
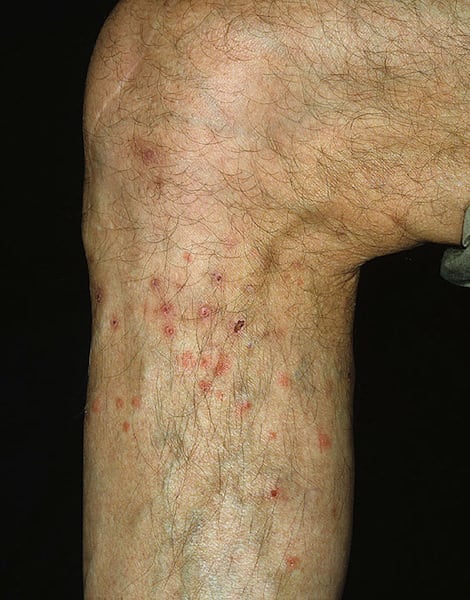
On the other hand, there are people who develop an immunity to flea bites if they’re bitten regularly. These people will only see a faint reddening of the bitten area, which often disappears within 15 minutes. They also do not experience any irritation as a result of the bites. This level of immunity is rare but does exist. For example, it’s commonly seen in tribal populations that live in flea-infested environments.
Side Effects and Symptoms of Flea Bites
The number one side effect of flea bites is intensive itching (pruritus). Bites can also be painful and become infected due to scratching. Some people experience a more intense reaction to flea bites than others. This is due to an extreme immune response to the presence of the chemicals in flea saliva.

Such an exaggerated response is known as “papular urticaria.” The area which has suffered the bite becomes very red, swollen and often has a blister in the center. If this becomes opened via scratching, the wound will become encrusted. People who suffer from this reaction may also find that old bites flare up again periodically.
Flea bites are generally found on the lower body; feet, ankles, and calves. Although, they can also be located around the waist area due to the high heights fleas can leap. The trouble with bites in these areas is that they can be further irritated by chafing from clothing, even if the victim is restraining themselves from scratching the bites.
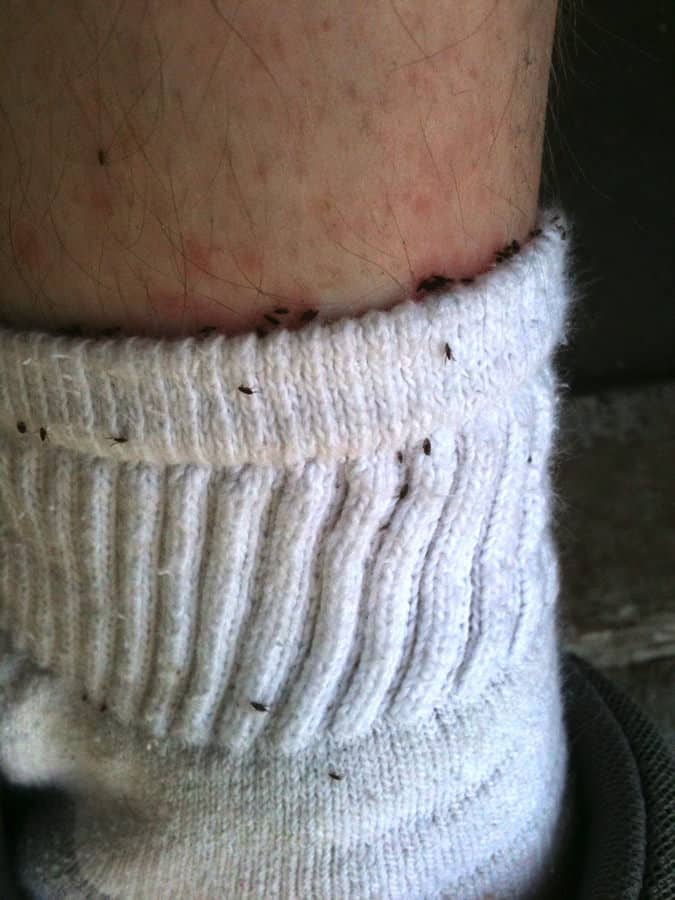
This may result in a more persistent reaction, where the itching stage is prolonged. One tip for preventing chafing is to dab some Vaseline on the bites, but only do this if you have to. It is much better to leave the bites open to the air to heal.
There are three main potential complications of flea bites to be aware of: allergic reactions, infections, and risk of disease. Serious allergic reactions are rare, but can be life-threatening. If a person who has been bitten by an insect presents the following symptoms, they must seek emergency treatment immediately:
- Difficulty breathing
- Nausea
- Swelling of lips and/or face
Flea bites can become infected if they are scratched, or rubbed open by clothing. Infections are painful and result in slower healing and scarring, but they can also present a risk of spreading and becoming more serious.
If a flea bite becomes warm to the touch, blistered, pus-filled, very painful and red, the victim should see a doctor. Antibiotics may be required to stop the infection from developing further and becoming more dangerous.
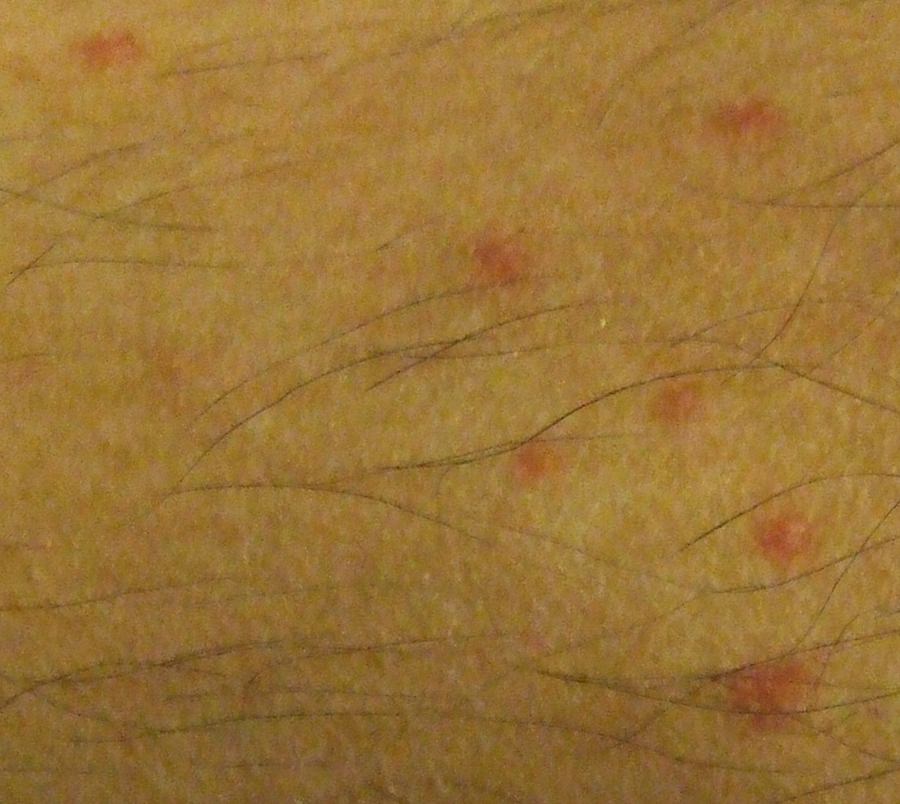
There are a number of diseases which can be transmitted by fleas to humans. Luckily, most of them are very rare in the US, but they are still occasionally reported.
Bubonic Plague
This is likely the most well-known disease associated with fleas. The bubonic plague, or “Black Death,” killed 25 million people in the 14th century. The bacterial infection is carried by rodents and transferred to the fleas which feed upon them.
Nowadays, the bubonic plague is still transmitted by fleas, but there are very few cases reported—mostly in the southwestern US states.
Bubonic plague is so-called due to the swollen lymph nodes, which are a key symptom of the disease. These develop around seven days after the victim is bitten by an infected flea.
Symptoms include:
- Swollen glands about the size of a chicken egg in the armpit, groin or neck
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches and pains
- Malaise
Bubonic plague can be effectively treated with antibiotics.
Tungiasis
This disease is much more common in the Caribbean, West Indies, and Central America, but it has been reported in the US too. Therefore, it’s a good idea to be aware of the symptoms.
Tungiasis is caused by a sand flea which “burrows” into the skin of the feet. It remains there while feeding on the host’s blood, producing eggs which are expelled into the environment. The lesions are swollen, itchy, and often look white with a black dot in the middle. Flesh necrosis can occur as a result of infection.
This condition is very rare, but should you see any of these symptoms, you must see a doctor immediately.
Murine Typhus
Southwestern states in the US receive a few reports of this disease every year, especially in areas which have a high rat population. Much like the bubonic plague, fleas which feed upon infected rats carry the bacteria with them, transferring it via their feces.
Scratching flea bites can transfer fecal matter from the flea into the wound. It can also be contracted by rubbing the eyes after touching flea feces. Infected flea feces can also be picked up from petting a dog or cat that harbors infected fleas.
Symptoms include:
- Fever
- Extreme headache
- Chills
- Nausea
- Weakness
Tularemia
Tularemia is a disease which is found naturally in North America. It is caused by the bacterium “francisella tularensis,” which can lead to a potentially serious infection. The bacteria is transmitted by the bite of an infected flea.
Symptoms include:
- Diarrhea
- Chills
- Pain in the joints
- Gradually increasing weakness
- Sudden fever
Medical treatment should be sought if you present any of these symptoms. Antibiotics are often required to treat this disease.
Summary
Flea bites are notorious for causing extreme irritation and itching, which can bring misery to you and your pet. If fleas have invaded your home, you’re almost certain to fall prey to their bloodsucking ways.
Even if you do not own any pets, you can still be at risk of flea bites from a friend’s pet, or even fleas who have made their way into your home from the yard.
Luckily, once you know how to identify flea bites, there are many cheap and easy ways to treat them at home. The most important takeaway is to do your best not to scratch the bites, no matter how itchy they are. Scratching flea bites not only increases the risk of infection and scarring, but in rare cases, it can contribute to the transmission of disease.
We hope the information contained in this article will help you to effectively spot flea bites, soothe the irritation, and prevent any further complications.