How Long Do Fleas Live Without A Host?
Fleas are tiny, resilient parasites which make their home among the fur of our much-loved pets. Their blood-sucking bites cause much distress and irritation, leading your pet to scratch themselves intensely.
What happens to the fleas which get dislodged from your furry friend? We all know that fleas can leap long distances, but in some cases, fleas are left unable to reach a host to feed on.
It is no secret that getting rid of fleas in your home can be a challenge. Understandably, some owners wonder whether temporarily removing their pet will ultimately starve any fleas which remain in the home.
In this article, we examine how long fleas can survive without access to a host.
Do Fleas Only Feed on Cats and Dogs?
Everyone knows that fleas are a problem for our beloved cats and dogs. However, some owners will wonder whether other creatures are also on the menu for fleas.
The truth is, fleas are not too picky about who they feed upon. They are notoriously opportunistic, so will attach themselves to most furry animals if they can. Fleas prefer warm-blooded creatures, primarily mammals, which have dense fur.
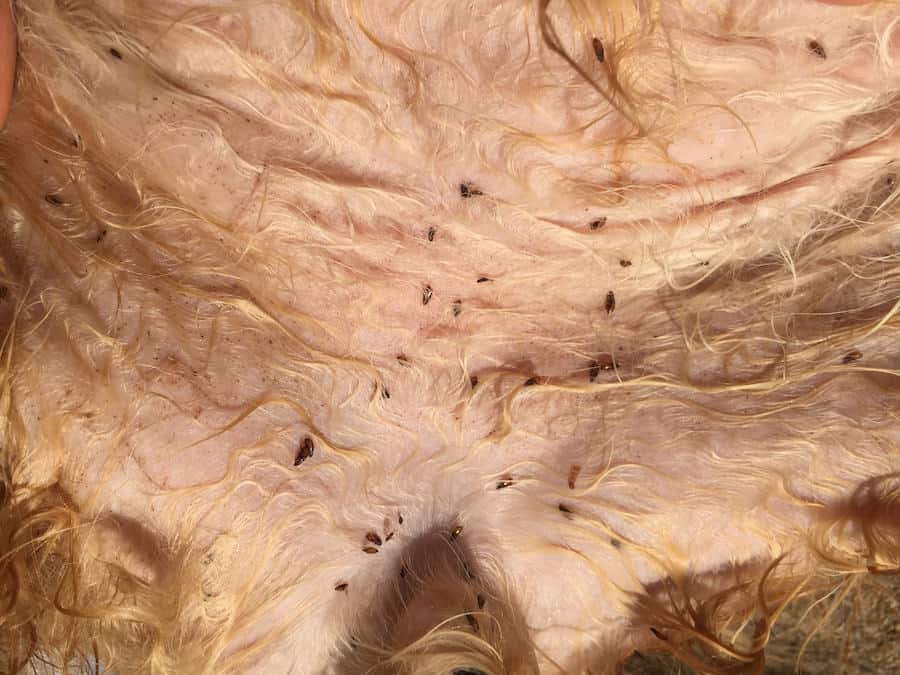
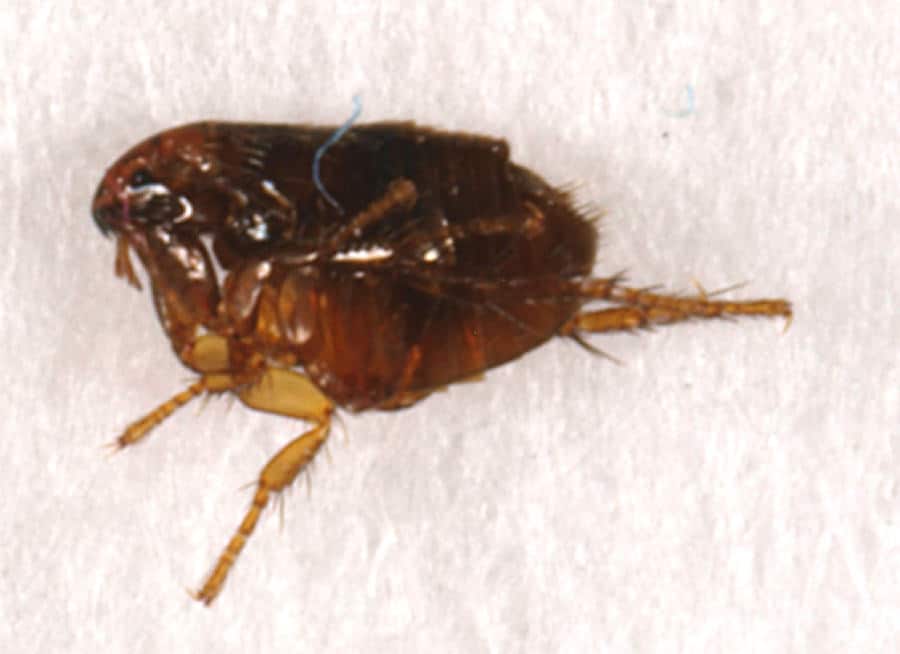
The most common flea found in US households is the cat flea, or “ctenocephalides felis”. Even though it is named as such, the cat flea will feed upon cats and dogs, as well as other mammals.

Cat fleas have been found on weasels, raccoons, rats, foxes, badgers and even deer.
In fact, it is their residence upon other creatures which often bring them into contact with your pet. The great majority of feral and urban wildlife will suffer from flea infestations. The fleas breed in their fur, laying eggs which drop to the ground wherever they go.

These animals frequently come into yards looking for food or shelter. The flea eggs will develop in the shaded areas where they have fallen. Once they have matured into adult fleas, they will quickly leap onto your pet when they walk past.
It is only adult fleas which live and feed on animals. Flea larvae and pupae stay hidden in the ground while they develop, surviving on organic matter.
How Often Do Fleas Usually Feed on a Host?
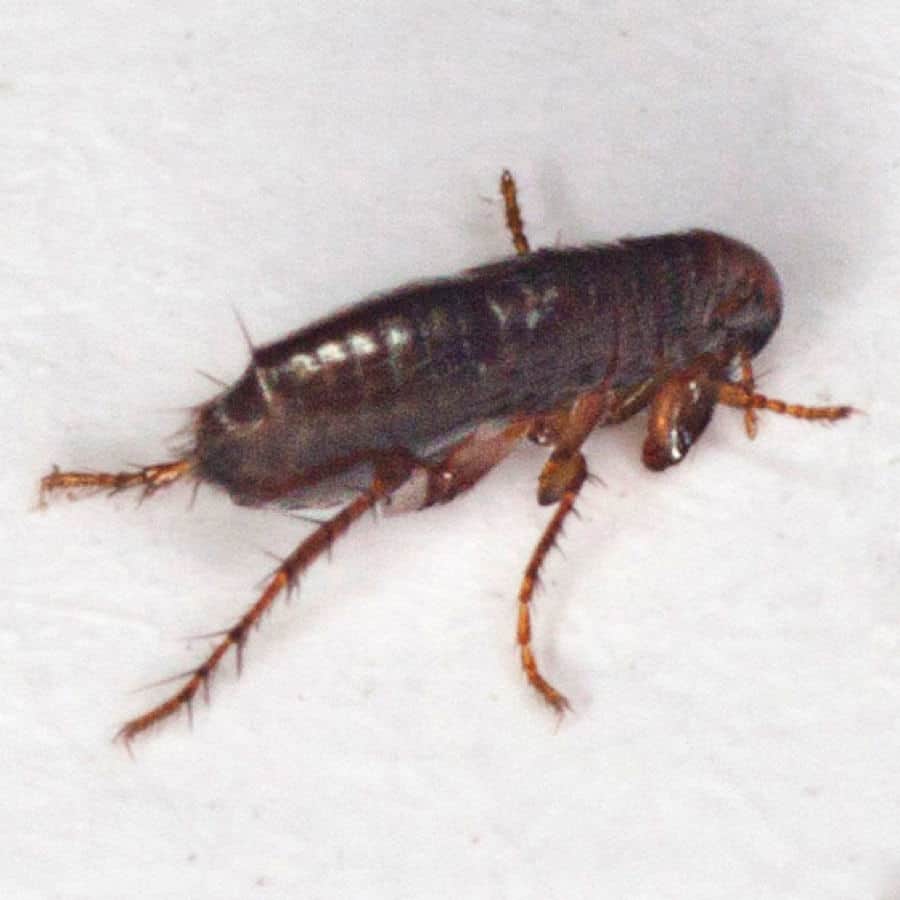
For such tiny creatures, fleas are formidable pests. They are only between 1/12 and 1/8 of an inch long, yet they can consume large quantities of blood relative to their size. A single flea will bite as many as 400 times every day.
If we consider that a flea can live up to 100 days, this adds up to as many as 4,000 bites per flea. It is little wonder that they drive our pets crazy.
A female flea is capable of producing up to 500 offspring over her lifetime. Studies have found that a single flea can multiply into a population of 1000 individuals, within as little as three weeks.

These figures do not take into consideration the eggs, larvae and pupae which will be developing at this time.

Fleas are able to consume large quantities of blood. Female fleas can engorge themselves to a greater degree than males.
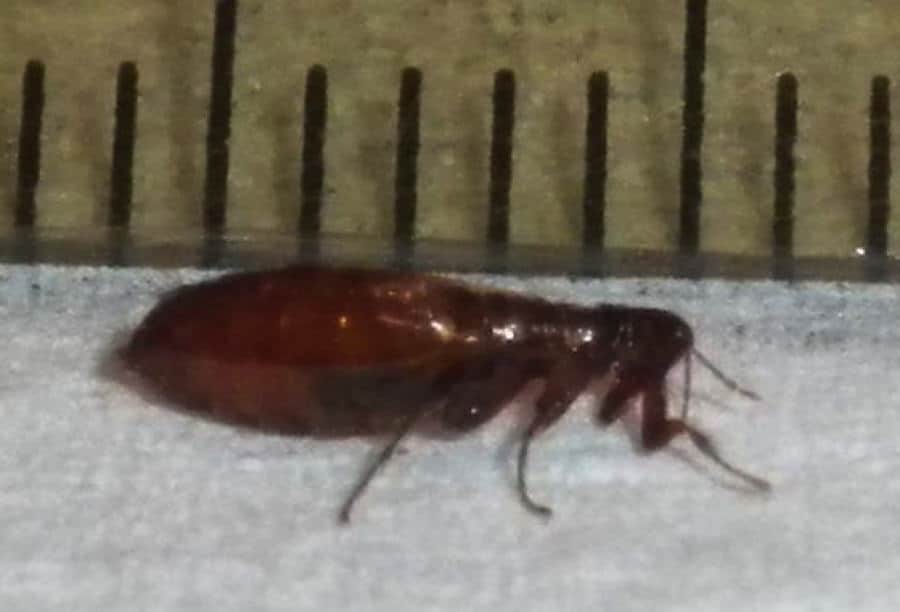

They employ specialized mouthparts to break the skin and then secrete anticoagulating saliva into the bloodstream. This action enables the flea to feed for as long as they wish.

In most cases, fleas will finish feeding between five minutes and one hour after biting. Female cat fleas can consume as much as 13.6 ul of blood per day.
This translates into more than 15 times their body weight. For this reason, kittens are very vulnerable to flea bites.
A young kitten weighing 1 pound will contain only about 30 ml of blood. Therefore, an intense flea infestation can rapidly deplete a kitten’s blood volume, causing anemia and death.
Within the course of five minutes, female fleas can easily ingest twice the blood volume of a male flea. Female fleas depend on the protein within the blood to be able to produce eggs.
During a normal feed, a male flea will usually ingest at least 15 percent less blood than a female.
Male fleas also feed for much shorter periods with every bite. 11 minutes per feed is common for male fleas. Females average a feeding time of 25 minutes per bite. If undisturbed, a female flea may continue to stay on a capillary for more than three hours.
How Long Can Fleas Live Without Feeding on a Host?
Once a flea has broken free from its pupal cocoon, it must have its first feed as soon as possible. If they fail, they will quickly succumb to starvation. On average, a flea must have a blood meal every 12 hours to remain healthy.
However, fleas are very resilient creatures. They are able to survive, if not thrive, without blood for relatively large periods of time. The amount of time they can endure depends almost entirely on the environmental conditions around them.
If they are newly emerged from a cocoon and have not yet fed, they are known as ‘unfed adults’. Unfed adults can often survive for longer than a flea which has been removed from its host.

Unfed adult fleas are more likely to survive in an environment which is humid. At 78 percent relative humidity, they have been observed surviving without a feed for up to 15 days. This duration is reduced to just over 12 days at 60 percent relative humidity.
If the ambient temperature is also cool, unfed fleas are able to survive even longer. In one laboratory study, unfed fleas lived as long as 40 days in such an environment.
Thankfully, this combination of cool temperatures and very high humidity is rare in real life.
Adult fleas choose to remain on their chosen host for the duration of their lives. They will not leave of their own volition, instead, they are often dislodged due to vigorous grooming.
A dislodged flea usually succumbs to starvation within a couple of days away from the host. This is due to ‘blood dependency’, a metabolic change which occurs once an adult flea has begun feeding regularly.

A study found that fleas which had recently emerged from their cocoon and fed upon a host for only five days, died within four days of removal.
If these newly emerged fleas were allowed to feed for only 12 hours, they did not reach a state of blood dependency. These restricted fleas were able to live for two weeks without blood when removed from their host.
Will Fleas Feed off Other Animals/Humans if Desperate?
Fleas are biologically hardwired to live and feed upon their preferred host. However, if they are desperate, fleas will certainly bite and feed upon humans or other mammals.
Fleas do not only live on dogs and cats. In fact, the pests currently residing in your home likely originated from other creatures. Flea infestations always begin outdoors.
Stray, feral and wild mammals frequently harbor fleas. These fleas breed and lay eggs among their fur, which drop to the ground as the host goes about their business.

It is very common for these animals to venture into your yard on their travels. Flea eggs are deposited on your property, quickly developing into hungry adult fleas. Before you know it, these fleas have latched onto your pet and taken a free ride indoors.
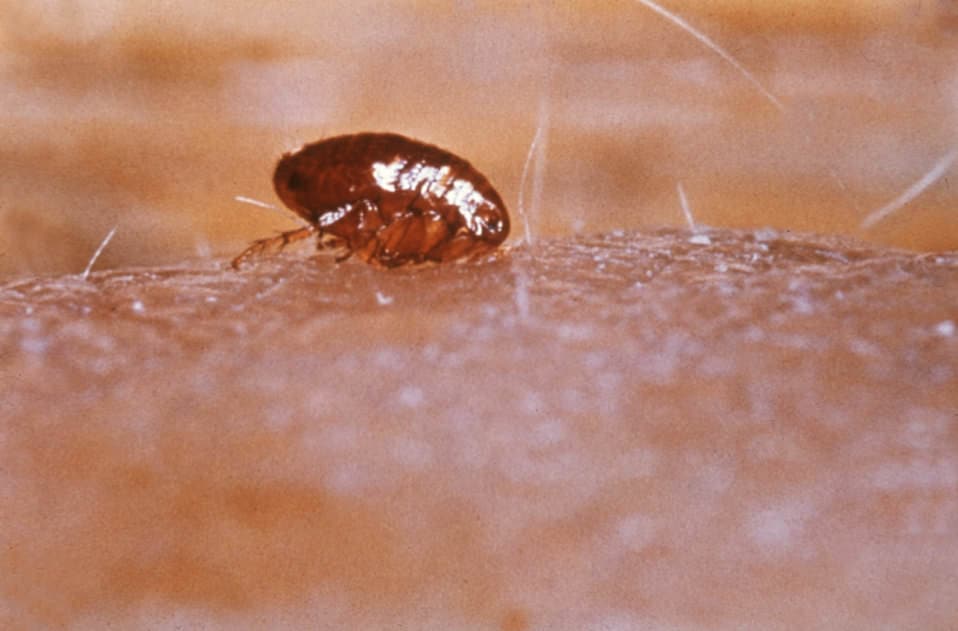
Flea bites on humans appear as small, raised, red bumps, which are normally grouped together. This is because a flea will engage in some ‘exploratory bites’ before finding the perfect spot.
Fleas are not fussy about where they bite, but humans are usually targeted around the lower body. Bites on the feet, ankles and calves are most common. This is simply because fleas are rarely able to reach any higher on our bodies.
Flea bites are certainly unpleasant. They can be extremely itchy, and pose a risk of infection if scratched too intensely. Luckily for us, fleas don’t really like to bite humans. Our blood can keep them alive, but it is not nutritious enough to support fertility.
This is why, even in the absence of pets, fleas do not choose to live on humans. They require a constant supply of preferred host blood to breed, so they will always be on the hunt for a more fitting host. They will simply bite humans to avoid starvation and then leave.

Furthermore, fleas are designed to hide, feed and move among dense fur. They despise direct light and feel far too exposed when feeding on human skin. Our lack of fur also makes us difficult to latch onto, so feeding for long periods becomes tiresome.
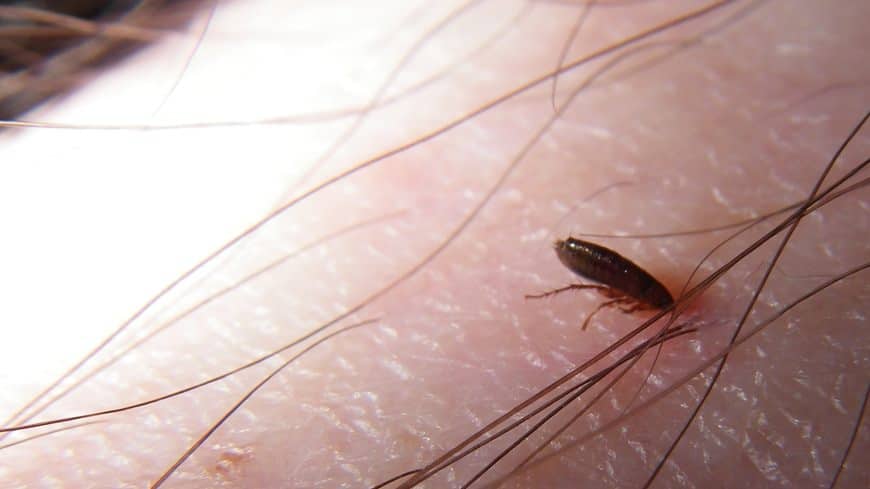

Overall, fleas will opportunistically feed upon humans and other furry animals if absolutely necessary, but they much prefer to live on your dog or cat.
Summary
As we have seen, the period of time which fleas can survive without a host can vary wildly. Environmental conditions, sex, and their developmental stage all affect how long a flea can withstand the lack of a host.
Removing a pet from your home is unlikely to starve fleas. These determined parasites will simply feed on you in the meantime to stay alive. The use of repellents on both you and your pet is an effective method to deny fleas a host.
Ultimately, all fleas will eventually succumb to starvation if there is no blood meal readily available. Under normal conditions, fleas are generally able to survive up to two weeks without a feed.